Congratulations to Dr. Shao-Yang Tsai, whose latest study has just been published in Cortex! This work investigates a fundamental question in attention research: how does the brain handle distractors that share key features with the target we are searching for?
In this high-density EEG study, participants performed a region-based visual search task where distractors either matched the target’s shape and color, differed by feature or dimension, or were presented in another modality (vibrotactile). Behavioral results showed that distractors sharing the critical target features caused the strongest interference, slowing responses more than other distractor types.
Electrophysiological analyses revealed a clear pattern:
- N2pc amplitudes were significantly larger only for same-feature distractors, indicating that these distractors successfully summoned spatial attention.
- Despite this attentional capture, there was no evidence of late PD (Distractor Positivity), meaning attention was not actively reoriented away after capture — suggesting no strong reactive suppression was necessary.
- CDA amplitudes were enhanced only for feature-matching distractors, reflecting their further registration in working memory.
- Ppc and CCN components confirmed early sensory registration of both visual and tactile distractors but ruled out Ppc as an index of early distractor suppression.
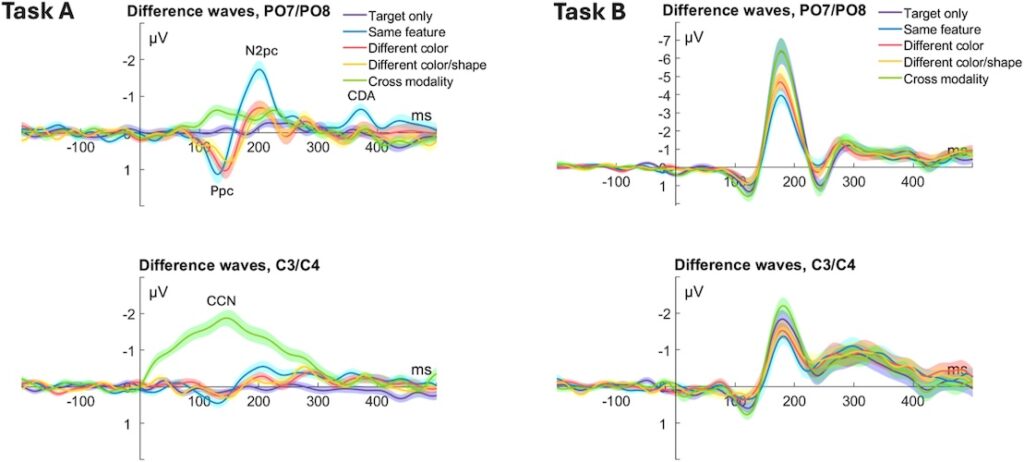
Taken together, these results support the “down-weighting” hypothesis: distractors are detected and registered but do not fully engage attentional resources. The spatial attentional template seems to function primarily by shielding distractor locations rather than enhancing target locations, ensuring efficient target selection without invoking strong suppression mechanisms.
Reference:
Tsai, S.-Y., Nasemann, J., Müller, H. J., & Shi, Z. (2025). Distractors sharing critical target features summon, but do not engage, attention: an EEG study. Cortex; a Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2025.07.017